
Not many people know this, and this is really important. Demand for US treasuries, especially the short (1 year) to mid-term (10 year) treasuries typically spike for 2 main reasons.
First, there is a genuine concern over the financial markets, for example, recessions and market corrections.
Second, the Fed increases the Federal Funds rates aggressively, which drives demand to hold US treasuries.
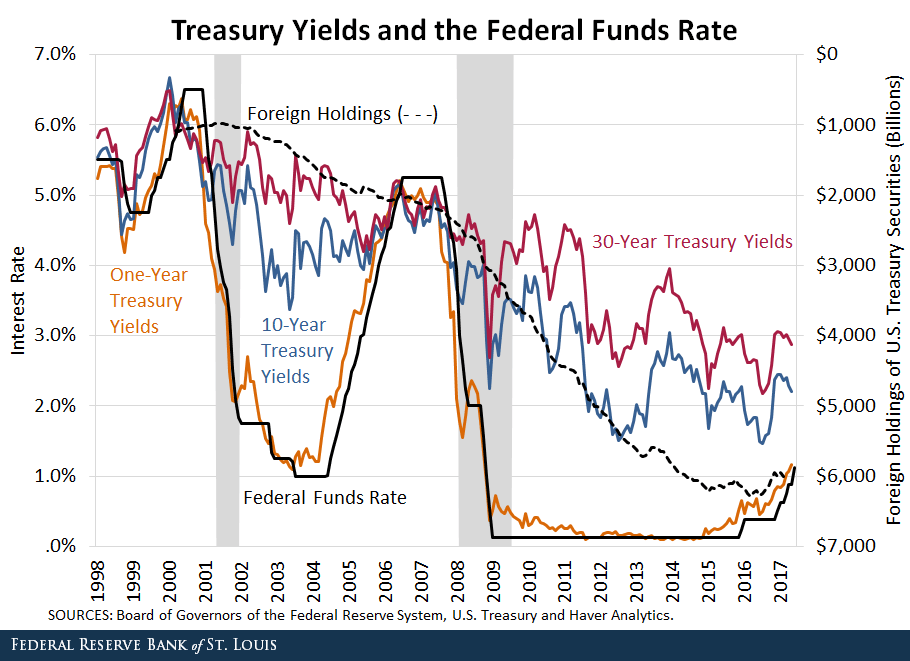
However, something really weird is happening right now. The Fed is aggressively hiking the Federal Funds Rate, yet the demand to hold US treasuries is low.
What exactly is happening here?
This article will present the facts to see what is happening under the hood of the financial markets.
Read on to find out more!
INTRODUCTION
In a nutshell, US treasuries are in low demand despite the Fed raising interest rates because of inflation.
To find a historical period of similar nature, we have to draw references the 1970s economic crisis. For example, the current high oil prices is similar to historically the 1970s which led to a kind of inflation called a “Cost-Push Inflation,” which means that the leading inflationary cause is the increase in the cost of production (in this case, the transportation cost).
It is a lose-lose economic scenario since inflation is not driven by increased demand or a decrease in supply. In this case, almost all of a country’s stakeholders (its population, businesses, and government institutions) would have to bear this.
But even if this is the case, how many of us genuinely remember or know how to invest and trade successfully in a 1970s market? Most of us haven’t even been born or are too young to be market participants during the period.
Therefore, most of us don’t have the luxury of experience to know how to adapt to this type of market environment. Thus, a fundamental understanding of economics behind this would help us decipher the best course of action moving forward.
SO WHY DOES THE US FEDERAL RESERVE RAISE INTEREST RATES?
Put simply, inflation causes the economy to expand, which is normal if it is within the range or target of the Federal Reserve. This kind of inflation would simply indicate a healthy growing economy.
However, if inflation is above the target of the Federal Reserve or it is simply too high, then prices of goods and services would drastically go up, causing the purchasing power of individuals and businesses to be less than what is desired.
To curb this, the federal reserve employs a tightening tool (in the form of raising interest rates) to restrict too much economic expansion.
WHY IS RAISING INTEREST RATES BAD NEWS TO THE MARKETS IN AN INFLATIONARY ENVIRONMENT?
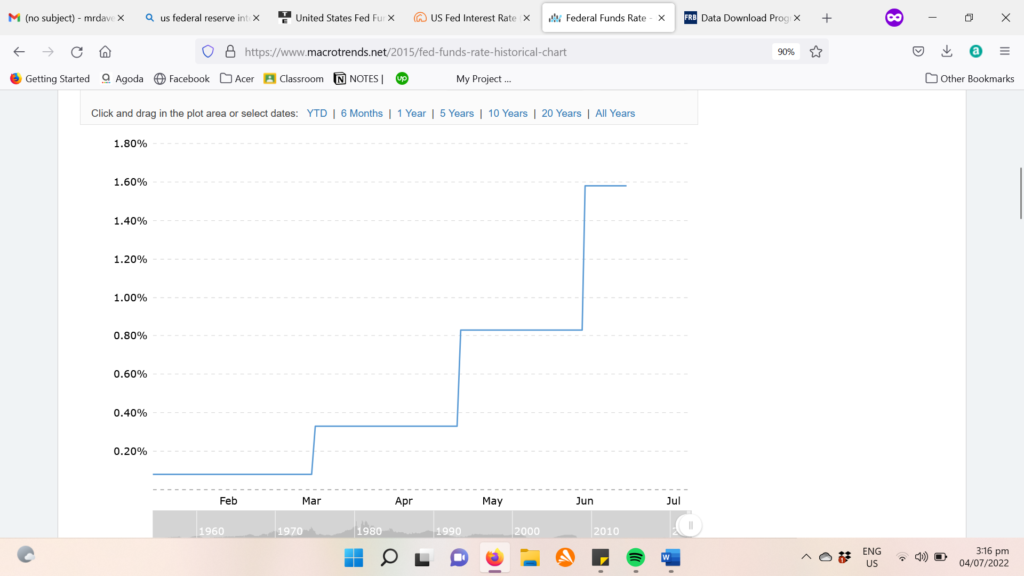
Source: Macrotrends.net
You can see that the interest rate looks like a staircase, consistently going up ever since the beginning of the year to its current rate range of 1.50% – 1.75%. Additionally, the Federal Reserve forecasts that it will need to raise interest rates by another 1.75% to meet its year-end target of at least 3.4%.
Now, if there is one thing the financial markets are most pessimistic of, it is rising interest rates. An interest rate hike discourages key expansionary economic activities such as borrowing, spending, and investing.
This means that businesses/companies will be hesitant to borrow for their expansion endeavors as borrowing costs will be higher. Moreover, businesses and individuals will also cut their spending and be more inclined to save.
Because of these two factors, it will then discourage investment in risky assets such as stocks since companies will generally experience lesser growth in this tightening economic environment. At the same time, the rates for “less risky” assets such as bonds, savings accounts, and government securities have decreased also because investing in these asset classes do not generate enough returns to beat inflation rates.
WHAT IS CREATING CONFUSION? IMPLICATIONS OF A POSSIBLE RECESSION
The biggest risk when the inflation is too high is that central banks also have to hike interest rates significantly. This is the case we are witnessing right now as the Federal Reserve aggressively hikes interest rates. On its most recent hike, it implemented an unprecedented rate increase of 0.75%, the highest in almost 30 years.
This increases the risk of a recession, which by its technical definition, is two quarters of sustained economic downturn. If recession indeed occurs, the expectation is that US securities, such as its treasury products, will offer a considerably higher rate while being a safer haven in economic downturns as the US government itself backs it. However, we are currently not seeing a rally in treasury yields yet.
Why? Well, this is because inflation remains high. It is crucial to remember that when central banks increase interest rates, the effect is not immediate. It could take months to years before the full effect on the economy takes place.
Therefore, an argument against investing in safer assets holds its bearing. The current high-interest rates economic environment will more likely behave differently from typical bear markets in the past.
High inflation encourages a portion of market participants with higher risk tolerance to find opportunities to beat the current inflation rate. Furthermore, US treasury yields do not offer attractive returns until it rallies, an event that will most likely only take place if the inflation rate has already peaked, so has it?
INFLATION MIGHT ALREADY BE PEAKING
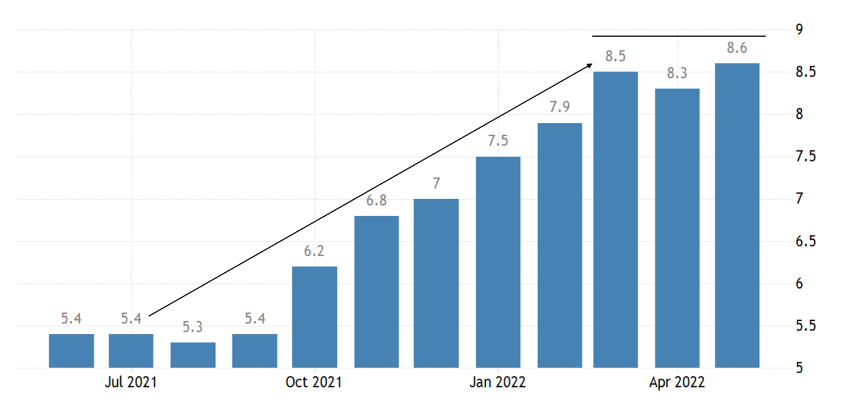
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Presented here is the monthly inflation rate. For the past three months, we have seen the inflation rate tapering off at around 8%—a far cry from the sustained increase we have seen in the previous months. On the 15th of June, the US Federal Reserve announced its largest interest rate hike in almost 30 years. Since 1994, a three-quarters of a percentage (0.75%) or 75 basis points rate increase has never been done by the US Central Bank in a single meeting until recently.
As mentioned earlier, the Federal Reserve forecasts to raise interest rates further to close at not less than 3.4% by the end of the year. This means the agency is looking to incrementally implement at least 175 basis points or an additional 1.75% spread across the four scheduled policy-setting meetings this second half of 2022.
This unprecedented tightening move by the US central bank could mark the peak of inflation.
Furthermore, markets are forward-looking. Hence, the next concern may be toward a possible recession caused by too much interest rates implemented too soon, especially if the net market participants view inflation as a thing of the past. Thus, investors may pivot back to US treasuries as a safe haven, especially if the narrative shifts towards a possible upcoming recession.
RATE MOVEMENT OF THE US TREASURY YIELD
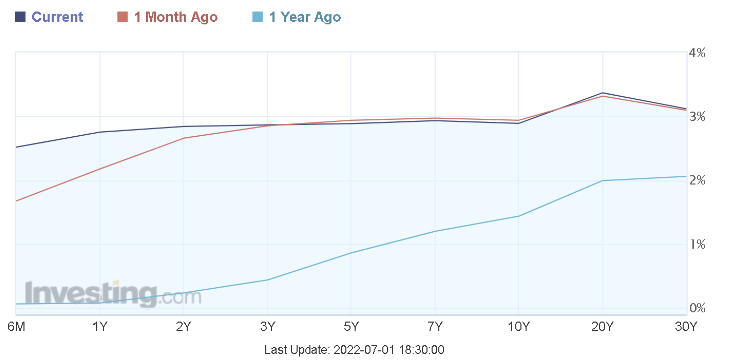
Source: Investing.com
Benefiting from the rising interest rate, the US Treasury yields seem to be consolidating and preparing for an upcoming correction. Please bear in mind that when US treasury yield drops, it signifies that demand for US treasuries will increase, and therefore US treasuries’ price will start to increase.
|
There is an inverse relationship between US Treasury YIELDS and US Treasury PRICES. |
As of the 1st of July, the two most extended timeframes, the 10-year Treasury return, gained 13.5 basis points in a month as it closed at 2.889%, while the longest-term 30-year bond rate gained 14.9 basis points closing at 3.116%.
As you can see, these figures are more than a 1% increase from a year ago. In addition, since the US Federal Reserve also indicated its plan of further increasing the interest rate by the second half of the year — this will likely prepare the US Treasury prices for an upcoming rally once inflation peaked.
WHEN WILL US TREASURIES BECOME AN INVESTABLE ASSET CLASS?
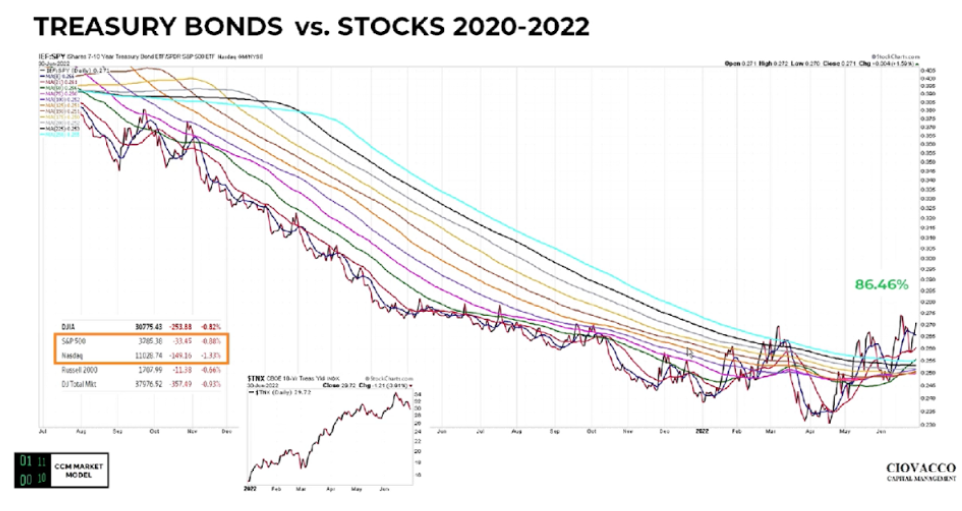
Source: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Aiu6_DQVSoA&t=684s
Therefore, the big question you may have is WHEN does the US treasury become attractive?
As you can see from the graph above, there is actually apparent evidence based on the price action movement that US treasuries are beginning to show higher demand compared to US stocks, represented by highlighted indices on the left (S&P 500 and Nasdaq).
NOTE: This price movement may suggest that the overall US market is slowly trying to pivot from being overly concerned about inflation toward the much-feared recession scenario caused by the “excessive” fed rate hikes, which were seen to be “too much too soon.”
Therefore, when the recession scenario begins to loom in the market as the “new big threat,” this could be a subtle shift in market sentiment as a possible massive transfer of funds away from risky assets such as stocks and towards a ‘safe haven’ type of investment during a recession – US treasury products.
Final Words
The US Federal Reserve, in response to the current high inflation, employs a tightening tool in the form of aggressive interest rate hikes.
The price action of US Treasuries has deviated from recent history. Historically, US treasuries’ demand increases when the Fed hikes interest rates.
This deviation is primarily caused by the current high inflation.
However, subtle changes under the hood have been detected, indicating that market sentiment is changing.
These changes may suggest a shift in risk perspective away from inflation and towards the looming recession.
Thus, if recession fear overwhelms market sentiment, a “flight to safety mentality” will take over. Therefore, it will encourage market participants to look for a “safe haven” investment in times of recession.
When this happens, US Treasuries are poised to be this “safe haven” investment during a recession, driving demand for the government securities back up.
Please note that all the information contained in this newsletter is intended for illustration and educational purposes only. It does not constitute any financial advice/recommendation to buy/sell any investment products or services.




